

Leading Solutions Provider for Healthcare Waste






BioSAFE Engineering has a rich 22-year history in the use of alkaline hydrolysis for waste decontamination. We hold a portfolio of patents that fuel alternative technologies to commercial incineration of pathological waste and diseased tissues. BioSAFE Engineering is a global leader in the design, manufacture, installation and service of equipment used among healthcare, research and industry players to eliminate the threat of hazardous or infectious agents. Our patented alkaline hydrolysis technology is the most cutting-edge biowaste decontamination technology on the market. It has been validated and recognized by the USDA, European Union, and the Canadian Food Inspection Agency for its ability to destroy and inactivate prion proteins. We carry products that offer significant benefits associated with minimizing or eliminating handling, transport and logistics by providing environmentally-safe treatment for decontamination and disposal of Regulated Medical Waste (RMW), Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) waste and other potentially-harmful waste. Our commercial waste treatment systems have processed over 2 billion tons of medical, commercial, agricultural and other potentially-infectious waste worldwide. The STI BioSAFE system supplied have shown to substantially lower operating costs and simplify compliance history with state and federal regulators.
Our Systems

Bio-containment

Anatomic Waste

Medical Waste

Crop Science
Effective Green Medical Waste Management
-
Every year approximately 16 billion injections are administered worldwide, but not all of the needles and syringes are properly disposed of afterwards.
-
Open burning and incineration of health care wastes can, under some circumstances, result in the emission of dioxins, furans, and particulate matter.
-
In 2015, a joint WHO/UNICEF assessment found that just over half (58%) of sampled facilities from 24 countries had adequate systems in place for the safe disposal of health care waste.
Challenges in healthcare waste management
-
Lack of awareness about the health hazards related to health-care waste, inadequate training in proper waste management, absence of waste management and disposal systems, insufficient financial and human resources and the low priority given to the topic are the most common problems connected with health-care waste. Many countries either do not have appropriate regulations, or do not enforce them.
Proper management of healthcare waste is important because :
-
The disposal of untreated health care wastes in landfills can lead to the contamination of drinking, surface, and ground waters if those landfills are not properly constructed.
-
The treatment of health care wastes with chemical disinfectants can result in the release of chemical substances into the environment if those substances are not handled, stored and disposed in an environmentally sound manner.
-
Incineration of waste has been widely practised, but inadequate incineration or the incineration of unsuitable materials results in the release of pollutants into the air and in the generation of ash residue. Incinerated materials containing or treated with chlorine can generate dioxins and furans, which are human carcinogens and have been associated with a range of adverse health effects. Incineration of heavy metals or materials with high metal content (in particular lead, mercury and cadmium) can lead to the spread of toxic metals in the environment.
-
High-income countries generate on average up to 0.5 kg of hazardous waste per hospital bed per day; while low-income countries generate on average 0.2 kg. However, health-care waste is often not separated into hazardous or non-hazardous wastes in low-income countries making the real quantity of hazardous waste much higher.
WHO Recommendation
WHO recommends the management of health-care waste requires increased attention and diligence to avoid adverse health outcomes associated with poor practice, including exposure to infectious agents and toxic substances. Key elements of WHO recommendation includes:
-
favouring the safe and environmentally sound treatment of hazardous health care wastes (e,g, by autoclaving, microwaving, steam treatment integrated with internal mixing, and chemical treatment) over medical waste incineration
-
building a comprehensive system, addressing responsibilities, resource allocation, handling and disposal. This is a long-term process, sustained by gradual improvements.
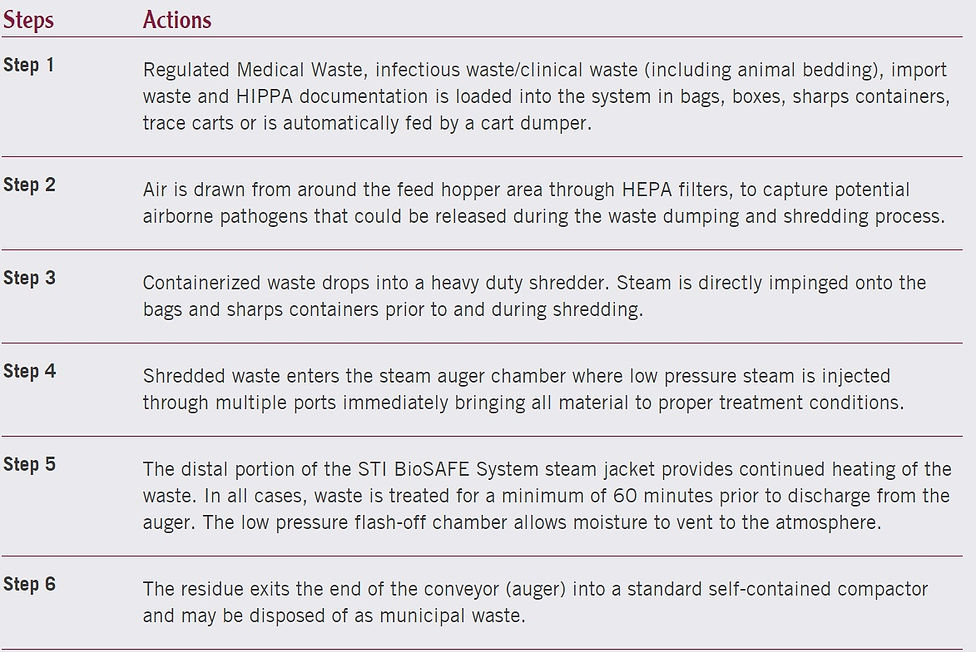
STI BioSAFE - How it works?
Effective Green Anatomical Waste Management
Outbreaks | Animal Research & Testing | Vaccine Research & Manufacturing
Chemistry of the Alkaline Hydrolysis Process
-
Decontamination
-
Sterilization
-
Biocontainment
-
Break Down of
Anatomical Waste
(Animal carcasses)
Hydrolysis is a process whereby chemical bonds are broken by the insertion of water between the atoms in the bond. Hydrolysis can be catalyzed by enzymes, metal salts, acids, or bases. Bases are typically water solutions of alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). Heating the reactants dramatically accelerates the hydrolysis reaction.
The process thus destroys all of these classes of compounds, reducing them to their building blocks and, in some cases, degrading them even further into smaller molecules. All proteins, regardless of their origin, are destroyed during the alkaline hydrolysis process.
Amino acids are linked to each other in a peptide (amide) bond in which the carboxyl group of one amino acid is condensed to the amino group of another amino acid with elimination of water. The resulting polymer is called a polypeptide or protein. All polypeptides consist primarily of the elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, along with smaller amounts of other elements, mainly sulfur and phosphorous. Hydrolysis reverses the condensation of amino acids into proteins by the acid- or alkali- catalyzed breaking of the peptide bonds and the addition of water at the break
Tissue Digesters - Alkaline Hydrolysis
BioSAFE Life Sciences' process uses alkaline hydrolysis at elevated temperature and pressure to convert the proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids of all cells and tissues, as well as infectious microorganisms, to a sterile aqueous solution of small peptides, amino acids, sugars, soaps, and electrolytes. The alkali itself is consumed in the process by generating the salts of the hydrolysis products. The only byproducts of the process are the mineral constituents of the bones and teeth of vertebrates. These are soft enough after the organic matter has been degraded to be easily crushed (even by bare hands) and recovered as calcium phosphate powder (sterile bone meal).
This process will:
-
Convert animal, human, and microbial tissues into a sterile, neutral,
aqueous solution suitable for disposal to a sanitary sewer. -
Sterilize and digests in one operation, reducing waste volume and weight
by up to 97% and completely destroying all known pathogens. -
Eliminate radioactivity contaminated tissues and neutralizes toxic fixing agents,
cytotoxic agents, and many other toxic compounds. -
Release NO materials to the atmosphere.
-
Operate at a fraction of the cost of an incinerator.
Tissue Digesters
Engineered Systems Capacity:
-
1500 lb Capacity
-
2000-3000 lb Capacity
-
4,000 lb Capacity Mobile
-
4000-6000 lb Capacity
-
7000-10000 lb Capacity
-
Cadaver
-
280 lb Tissue Digester/EDS Combo
Standard Systems Capacity:
-
11 lb Capacity
-
30 lb Capacity
-
45 lb Capacity
-
80 lb Capacity
-
200-300 lb Capacity
-
500 lb Capacity
Dehydrator Features Include:
-
Scalable for all BioSAFE Engineering Tissue Digester Systems
-
Steam-heated
-
Collector Tank and Discharge Bin
-
Adjustable Processing Rates / Moisture Content
-
Operates Autonomously from the Tissue Digester
-
Vacuum Odor Control System with 0.2 um Hydrophobic Exhaust Filter
Effective Green Effluent Waste Management
Effluent Decontamination
Effluent Decontamination Systems (EDS) are required to treat all laboratory wastewater/effluent produced within biocontainment boundaries. This effluent typically originates from the laboratory sinks, showers, floor drains, and autoclaves. EDS are recommended, and/or required by law, across the world for facilities classified as Bio-safety Level 3 and Level 4 (BSL-3 and 4).
Effluent Decontamination Systems use a combination of heat and pressure to ensure that any potentially dangerous microbiological agents in the effluent are destroyed before release to the public sewer. Effluent Decontamination Systems can operate as continuous or as a continuous-batch process, the latter of which is the chosen standard for our systems due to the inherent safety control and containment advantages.
BioSAFE Life Sciences also produce stand alone EDS. We offer a wide selection of configurations and capacities and are designed to treat thousands of gallons per day. EDS can be sized for any facility from a single laboratory room to a large multi-user facility. We also offer a unique "prion cycle" feature, incorporating our patented Alkaline Hydrolysis technology, for the safe disposal of potentially TSE infected effluent.



.png)




